What is DMARC?
How DMARC Works?
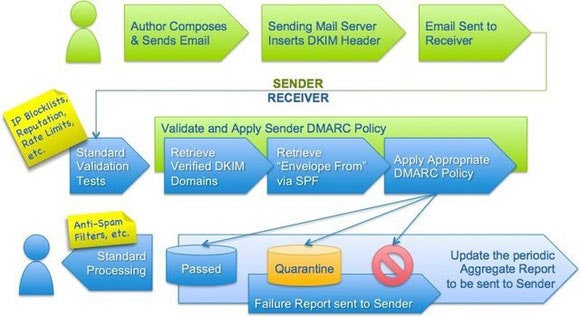
- User composes an email and send with the DKIM header inserted by the sender server.
- DMARC matches the header from domain name with the envelope from domain name used during an SPF record check.
- DMARC matches the header from domain name with the d= domain name in the DKIM signature.
- To pass the DMARC authentication, received message must pass the SPF authentication/ alignment and/or DKIM authentication/alignment. When the message fails both SPF/SPF alignment and DKIM/DKIM alignment, the DMARC will get failed and it will instruct email providers on how to handle unauthenticated mail via a DMARC policy. According to the DMARC policy you set, senders can either:
- Monitor all mail ensuring all legitimate mail are authenticating properly without interfering with the delivery of messages that fail DMARC.
- Quarantine messages that fail DMARC.
- Reject messages that fail DMARC.
DMARC Tags
DMARC policies are published in the DNS as a text (TXT) records and announce what an email receiver should do with non-aligned. Consider the following example.
"v=DMARC1;p=reject;pct=100;rua=mailto:[email protected]"
| Tag Name | Purpose | Sample |
| v | Protocol version | v=DMARC1 |
| pct | Percentage of messages subjected to filtering | pct=20 |
| ruf | Reporting URI for forensic reports | ruf=mailto:[email protected] |
| rua | Reporting URI of aggregate reports | rua=mailto:[email protected] |
| p | Policy for organizational domain | p=quarantine |
| sp | Policy for subdomains of the OD | sp=reject |
| adkim | Alignment mode for DKIM | adkim=s |
| aspf | Alignment mode for SPF | aspf=r |
Create DMARC Record
Once you setup the SPF and DKIM records, you can configure the DMARC by following below DMARC wizard with appropriate name and value. Again, DMARC policies are published in the DNS as text (TXT) record. So once your DMARC record is ready, you can add it as a TXT record in your DNS zone.



























